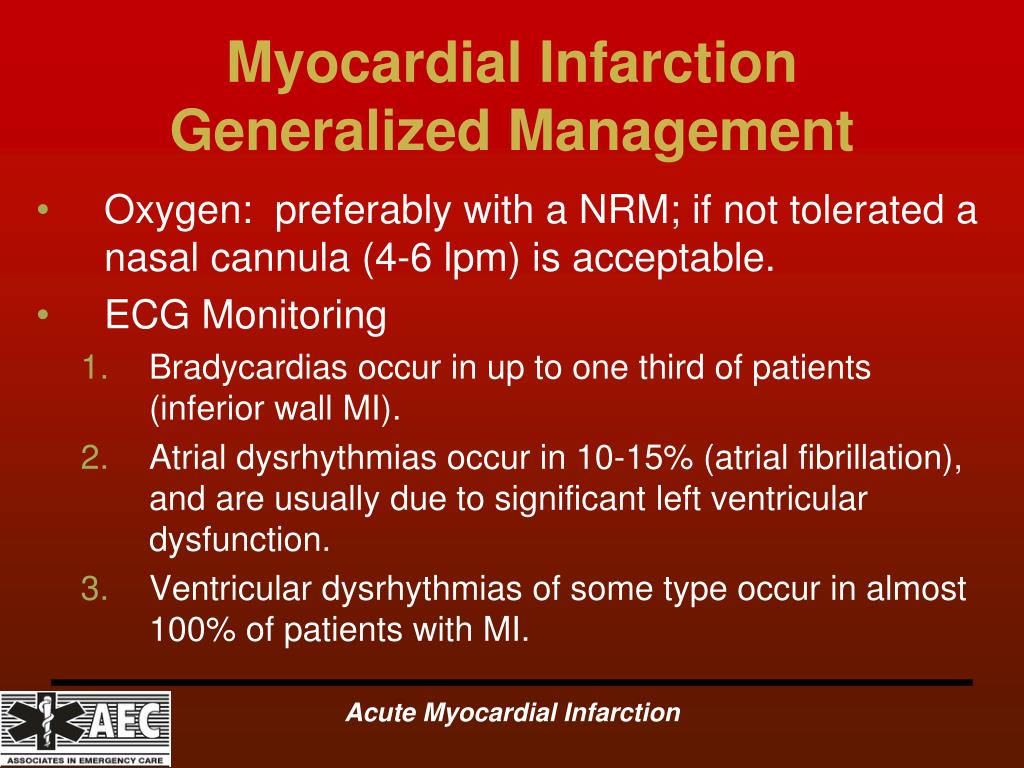
Inferior Wall Mi Treatment
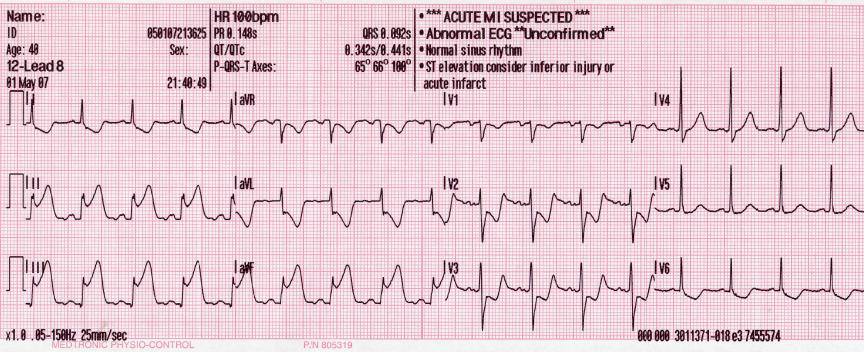
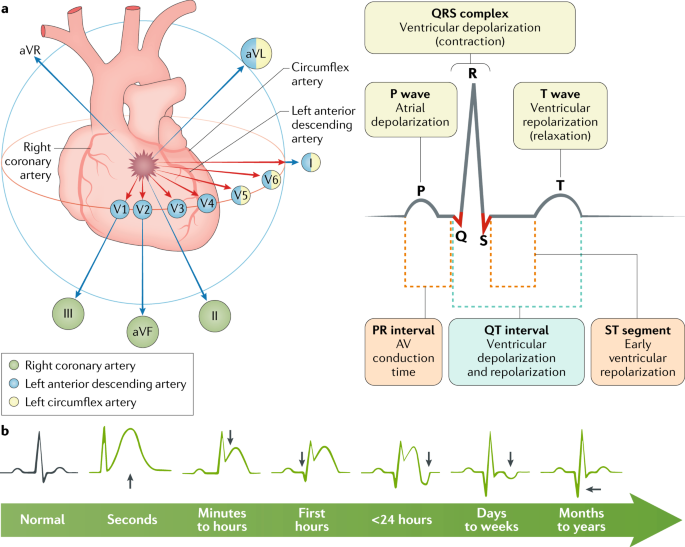
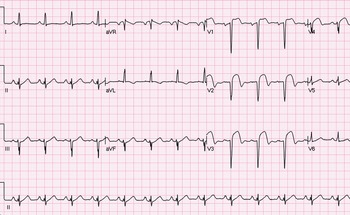
Inferior wall mi treatment. Inferior wall myocardial infarction MI occurs from a coronary artery occlusion with resultant decreased perfusion to that region of the myocardium. Oxygen aspirin nitrates and triage to an appropriate medical center Drug treatment. An inferior wall MI should be diagnosed with certainty only when abnormal Q waves are seen in leads II III and aV F.
Nitroglycerin or opioids may be used to help with chest pain. The classic features of inferior STEMI are unmistakable. Cal MI is no better than that for patients with unrecog nized MI.
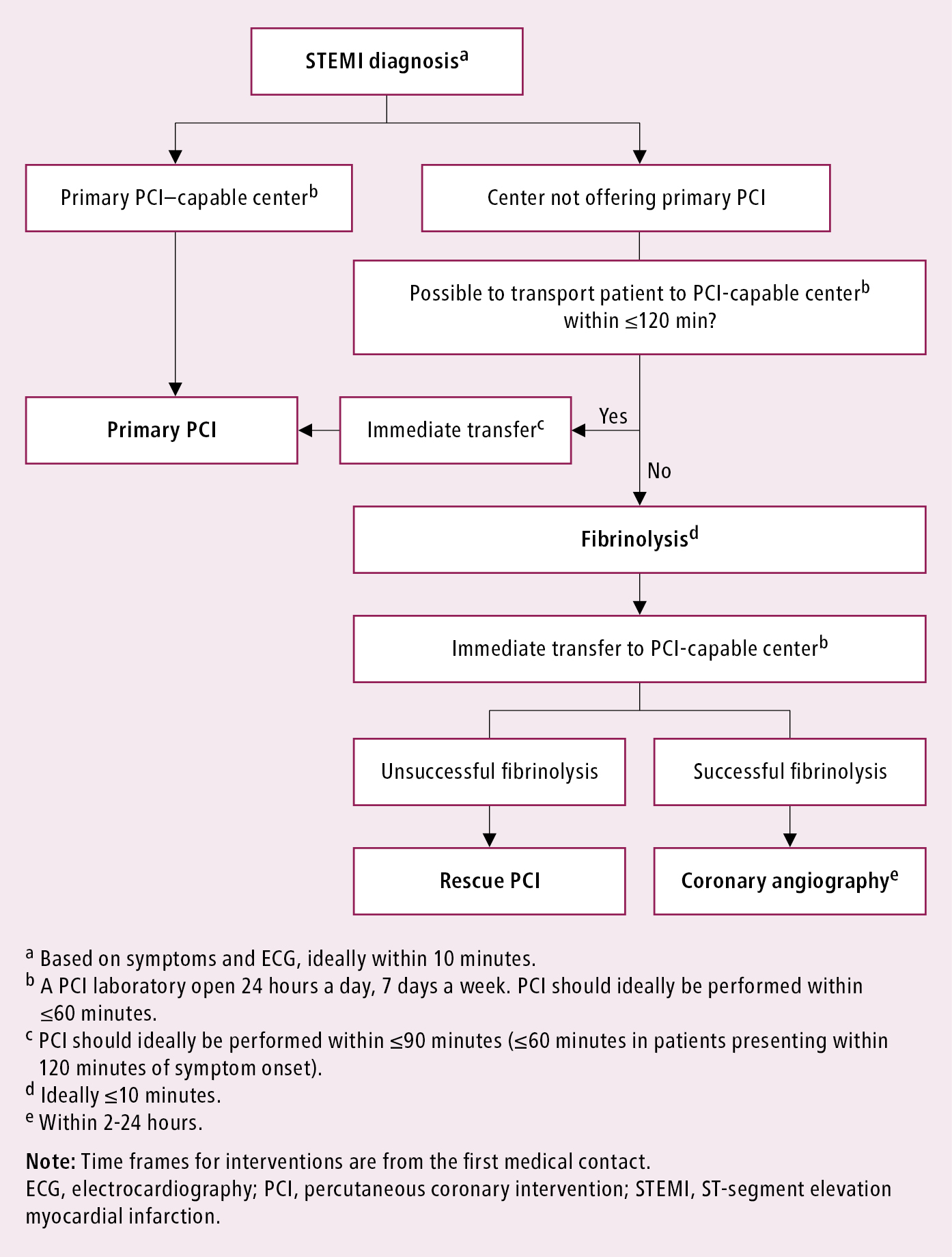
In most cases there is reciprocal ST-segment depression in the high. Primary percutaneous coronary intervention is nowadays the preferred reperfusion strategy for patients with acute ST-segmentelevation myocardial infarction aiming at restoring epicardial infarct-related artery patency and achieving microvascular reperfusion as early as possible thus limiting the extent of irreversibly injured myocardium. The availability of mechanical support and percutaneous closure has significantly altered the treatment paradigm.
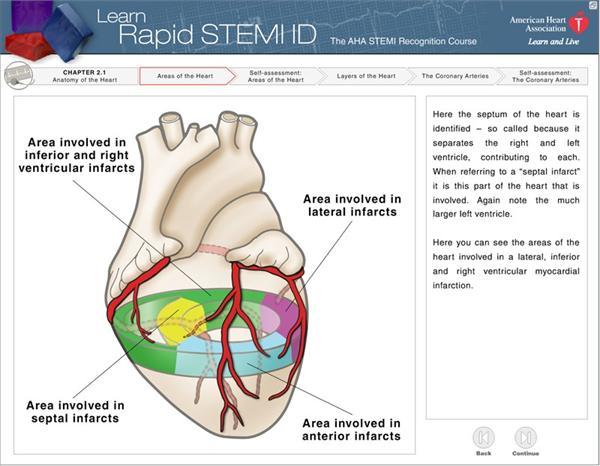
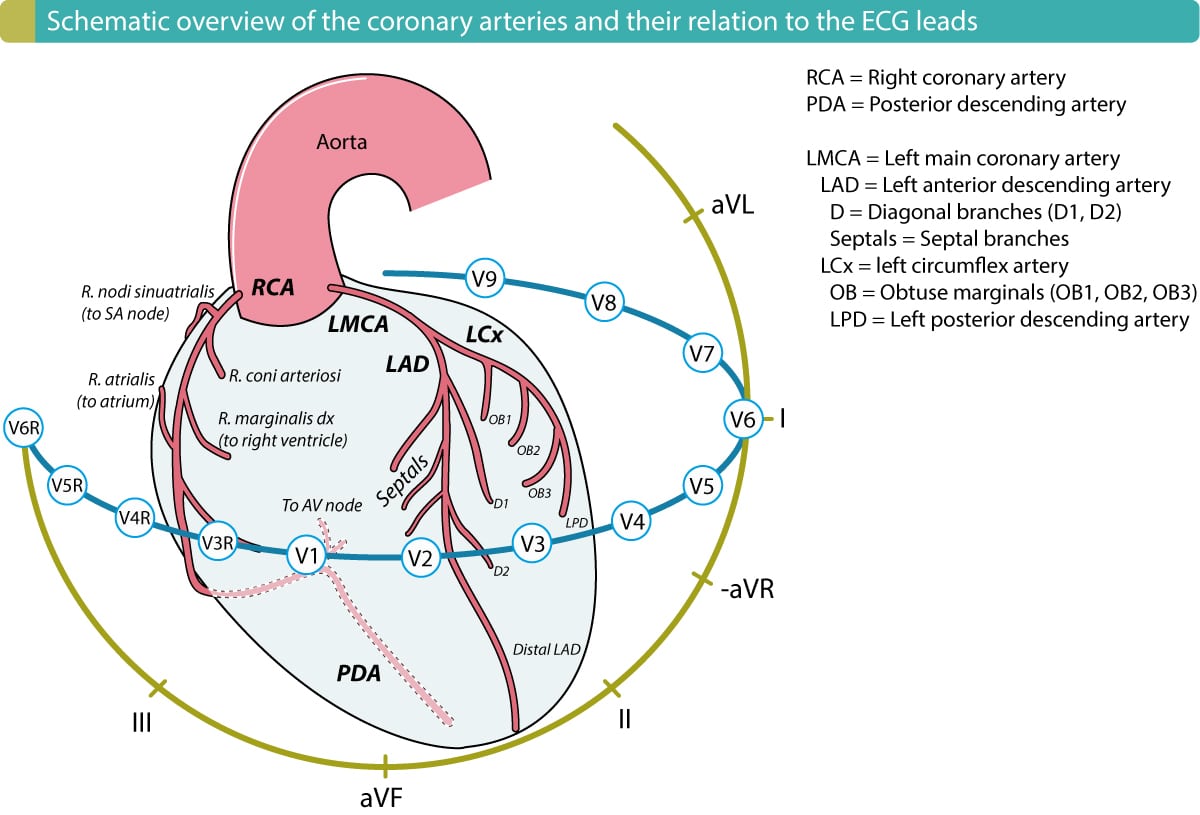
The Right Coronary Artery RCA usually supplies this part of the ventricle but in about 20 of cases the circumflex artery a branch of the left coronary artery wraps all the way around the left ventricle and supplies the inferior wall. Inferior wall myocardial infarction stems from ischemia and necrosis due to occlusion of the right coronary andor distal circumflex arteries that. Surgery can also be an option.
In this setting ST-segment depressions appear in the right precordial leads V1 V2 and V3 along with classic ST-segment elevations in the inferior leads. An anterior wall MI should not be diagnosed from lead aV L alone. Unless there is timely treatment this results in myocardial ischemia followed by infarction.
Posterior wall ST-elevation myocardial infarction commonly occurs as a complication or extension of acute inferior wall STEMI. Patients may be given supplementary oxygen if they have trouble breathing. Intravenous diamorphine 255 mg repeated as necessary is the drug of choice and is not only a powerful analgesic but also has a useful anxiolytic effect.
In most patients the inferior myocardium is. Treatment of Acute MI Prehospital care.
Aspirin is an appropriate immediate treatment for a suspected MI.
In most patients the inferior myocardium is supplied by the right coronary artery. Inferior wall myocardial infarction stems from ischemia and necrosis due to occlusion of the right coronary andor distal circumflex arteries that. Treatments for inferior myocardial infarction can include the administration of medications along with rest. Inferior wall myocardial infarction IMI is the most common ST-elevation myocardial infarction STEMI. Inferior wall myocardial infarction MI occurs from a coronary artery occlusion with resultant decreased perfusion to that region of the myocardium. Inferior Myocardial Infarction Inferior Infarction. In most patients the inferior myocardium is supplied by the right coronary artery. This can cause a ST elevation myocardial infarction or a non-ST segment elevation myocardial infarction. Patients with inferior-wall MI presented more of.
Supplemental oxygen is recommended in those with low oxygen levels or shortness of breath. Ventricular septal rupture VSR remains a devastating complication following acute myocardial infarction MI. Surgical repair is the definitive treatment but it is challenging and associated with high morbidity and mortality. Oxygen aspirin nitrates and triage to an appropriate medical center Drug treatment. Treatments for inferior myocardial infarction can include the administration of medications along with rest. The precordial ST-segment depressions are the mirror image of. In this setting ST-segment depressions appear in the right precordial leads V1 V2 and V3 along with classic ST-segment elevations in the inferior leads.






































Posting Komentar untuk "Inferior Wall Mi Treatment"