Papillon-lefevre Syndrome
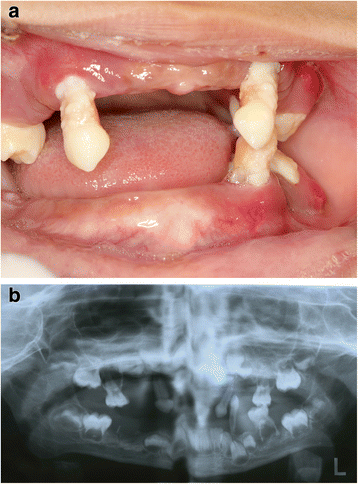
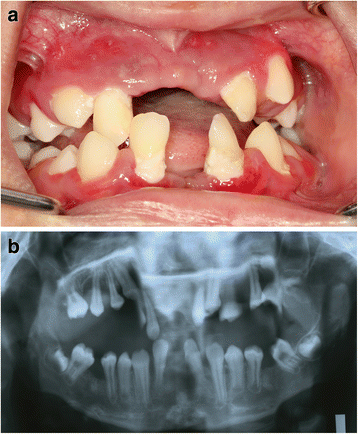
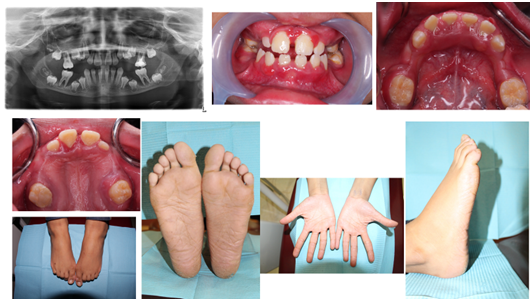
Papillon-lefevre syndrome. Papillon and Paul Lefèvre in France. Papillon-Lefévre syndrome is a rare inherited autosomal-recessive disease characterized by palmoplantar keratosis and severe prepubertal periodontitis leading to premature loss of all teeth. Various etiopathogenic factors are associated.
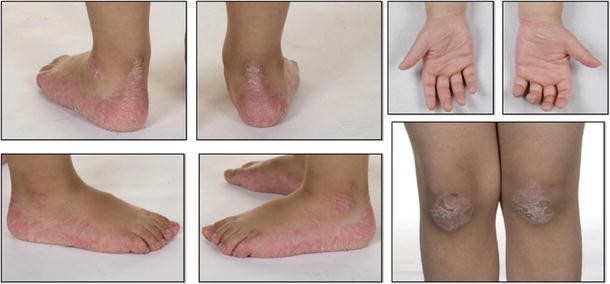
PapillonLefevre syndrome PLS is a rare autosomal recessive disorder of keratinization characterized by palmoplantar hyperkeratosis periodontal involvement and precocious loss of dentition. Introduction PapillonLefèvre syndrome PLS was first described by two French physicians M. Papillon-Lefèvre syndrome is a very rare syndrome of autosomal recessive inheritance characterized by palmar-plantar hyperkeratosis and early onset of a severe destructive periodontitis leading to premature loss of both primary and permanent dentitions.
Cathepsin C is necessary for granzyme B and. Papillion-Lefevre syndrome is an autosomal recessive disorder characterized by palmoplantar keratoderma periodontitis and premature loss of dentition summary by. What is Papillon-Lefevre Syndrome PLS.
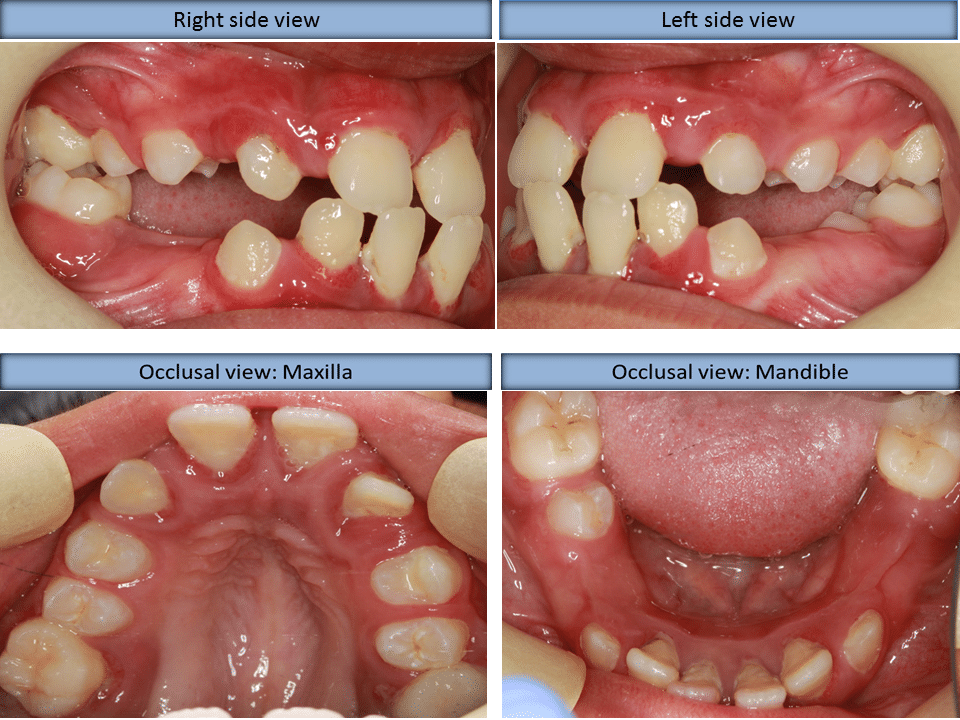
Papillon-Lefèvre syndrome PLS is a rare autosomal recessive genetic disorder caused by cathepsin C deficiency. The condition leads extensive damage to the periodontium the tissue that surround and support the teeth and early loss of milkand permanent dentition. Papillion-Lefevre syndrome is an autosomal recessive disorder characterized by palmoplantar keratoderma periodontitis and premature loss of dentition summary by Lefevre et al 2001.
The syndrome is characterized by palmoplantar keratoderma and destructive periodontal disease which manifests as gingival inflammation and loss of most primary and permanent teeth. The Papillon-Lefèvre syndrome is characterized by palmar-plantar hyperkeratosis and periodontosis occurring in childhood after the eruption of deciduous teeth. PapillonLefèvre syndrome PLS is a rare autosomal recessive disorder characterized by diffuse palmoplantar keratoderma and precocious aggressive periodontitis leading to premature loss of deciduous and permanent dentition at a very young age.
32 rows Papillon-Lefèvre syndrome PLS is a rare ectodermal dysplasia. Papillon-Lefèvre syndrome is a very rare syndrome of autosomal recessive inheritance characterized by palmar-plantar hyperkeratosis and early onset of a severe destructive periodontitis leading to. PapillonLefèvre syndrome PLS is a very rare autosomal recessive disorder characterized by palmoplantar hyperkeratosis and severe early onset periodontitis affecting the primary and permanent dentition.
Additionally associated findings of calcification of the choroid plexus and tentorium have been reported in. Papillon-Lefévre syndrome PLS is a very rare autosomal recessive trait characterized by palmoplantar hyperkeratosis and severe generalized early-onset periodontitis leading to premature loss of both primary and permanent dentitions.
Papillon-Lefèvre syndrome is a very rare syndrome of autosomal recessive inheritance characterized by palmar-plantar hyperkeratosis and early onset of a severe destructive periodontitis leading to premature loss of both primary and permanent dentitions.
Papillon-Lefèvre syndrome is a very rare syndrome of autosomal recessive inheritance characterized by palmar-plantar hyperkeratosis and early onset of a severe destructive periodontitis leading to. Papillon-Lefèvre syndrome is a very rare syndrome of autosomal recessive inheritance characterized by palmar-plantar hyperkeratosis and early onset of a severe destructive periodontitis leading to premature loss of both primary and permanent dentitions. Papillon Lefevre syndrome is a disorder characterized by excessive production of keratin on the palms and soles in combination with severe periodontal destruction. Papillion-Lefevre syndrome is an autosomal recessive disorder characterized by palmoplantar keratoderma periodontitis and premature loss of dentition summary by. Papillon-Lefévre syndrome is a rare inherited autosomal-recessive disease characterized by palmoplantar keratosis and severe prepubertal periodontitis leading to premature loss of all teeth. Introduction PapillonLefèvre syndrome PLS was first described by two French physicians M. The Papillon-Lefèvre syndrome is characterized by palmar-plantar hyperkeratosis and periodontosis occurring in childhood after the eruption of deciduous teeth. Papillon-Lefèvre syndrome PLS is an extremely rare genetic disorder that typically becomes apparent from approximately one to five years of age. Papillon-Lefévre syndrome PLS is a very rare autosomal recessive trait characterized by palmoplantar hyperkeratosis and severe generalized early-onset periodontitis leading to premature loss of both primary and permanent dentitions.
What is Papillon-Lefevre Syndrome PLS. The Papillon-Lefèvre syndrome is characterized by palmar-plantar hyperkeratosis and periodontosis occurring in childhood after the eruption of deciduous teeth. The syndrome is characterized by palmoplantar keratoderma and destructive periodontal disease which manifests as gingival inflammation and loss of most primary and permanent teeth. PapillonLefèvre syndrome PLS is a rare autosomal recessive disorder characterized by diffuse palmoplantar keratoderma and precocious aggressive periodontitis leading to premature loss of deciduous and permanent dentition at a very young age. What is Papillon-Lefevre Syndrome PLS. Papillon-Lefèvre syndrome PLS is a rare autosomal recessive genetic disorder caused by cathepsin C deficiency. The condition leads extensive damage to the periodontium the tissue that surround and support the teeth and early loss of milkand permanent dentition.









































Posting Komentar untuk "Papillon-lefevre Syndrome"